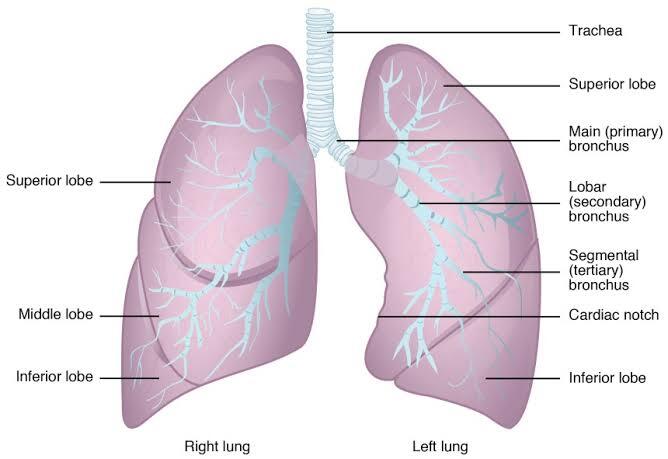
Humans have two lungs, one on the left and one on the right. They are situated within the thoracic cavity of the chest. The right lung is bigger and heavier than the left, which shares space in the chest with the heart. The lungs together weigh approximately 1.3 kilograms (2.9 pounds). The lungs are part of the lower respiratory tract that begins at the trachea and branches into the bronchi and bronchioles, and which receive air breathed in via the conducting zone. The conducting zone ends at the terminal bronchioles. These divide into the respiratory bronchioles of the respiratory zone which divide into alveolar ducts that give rise to the alveolar sacs that contain the alveoli, where gas exchange takes place. Alveoli are also sparsely present on the walls of the respiratory bronchioles and alveolar ducts. Together, the lungs contain approximately 2,400 kilometres (1,500 miles) of airways and 300 to 500 million alveoli. Each lung is enclosed within a pleural sac of two membranes called pleurae; the membranes are separated by a film of pleural fluid, which allows the inner and outer membranes to slide over each other whilst breathing takes place, without much friction. The inner pleura also divides each lung into sections called lobes. The right lung has three lobes and the left has two. The lobes are further divided into bronchopulmonary segments and pulmonary lobules. The lungs have a unique blood supply, receiving deoxygenated blood from the heart in the pulmonary circulation for the purposes of receiving oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide, and a separate supply of oxygenated blood to the tissue of the lungs, in the bronchial circulation. Deoxygenated blood travels from the heart through the pulmonary artery to the lungs to be oxygenated in capillaries of alveoli. After the blood is oxygenated, it returns to the heart through the pulmonary vein to be sent to the rest of the body