Are you prepared for Earth's weakening magnetic field?
🌍
THE EARTH DISASTER CYCLE,
by Keyvan Davani.
THE EARTH DISASTER CYCLE
Earth’s Geomagnetic Cycles and the Coming Shift: A Scientific Perspective
Earth’s Magnetic Field Is Changing — What It Means for Us
Earth’s magnetic field is like an invisible force field, protecting life from cosmic radiation and guiding compasses, birds, and even whales. But this shield isn’t constant. It shifts, weakens, and sometimes even flips. Scientists say these changes follow natural cycles — and the next big shift may already be underway.
A Clock Ticking in Earth’s History
Geological records show repeating patterns: - About every 6,000 years, the magnetic field weakens significantly. - About every 12,000 years, the changes are more severe, sometimes linked to mass extinctions and climate upheavals. We are more than 6,000 years past the last event, which places us right in the window for the next one.
Signs It’s Already Happening
- The poles are racing: The north magnetic pole is moving toward Siberia at up to 60 km per year. The south pole is sliding out of Antarctica toward the Indian Ocean. - The field is weakening: Since the 1800s, Earth’s field has lost more than 15% of its strength. - The South Atlantic Anomaly: A weak spot over South America exposes satellites to higher radiation.
Why It Matters
A weaker magnetic field brings ripple effects: - More radiation enters the atmosphere, damaging ozone and letting in harmful UV. - Climate disruptions can follow, as the balance of energy shifts. - Biosphere stress: Past shifts line up with extinction pulses. - Technology at risk: A solar storm during weakened field conditions could cripple satellites, GPS, and power grids.
What If a Solar Superstorm Hits?
The last major solar storm — the Carrington Event of 1859 — set telegraph lines on fire. If such a storm struck today, with our weakened magnetic shield, the results could be devastating.
What We Can Do
We can’t stop Earth’s cycles, but we can prepare: - Harden power grids and satellites. - Secure food and water systems. - Strengthen local communities. - Support research into space weather and geomagnetic science.
The Bigger Picture
Earth has survived countless magnetic shifts before — but humanity’s global technology makes this one different. Awareness isn’t about fear. It’s about readiness. Awareness = Readiness.
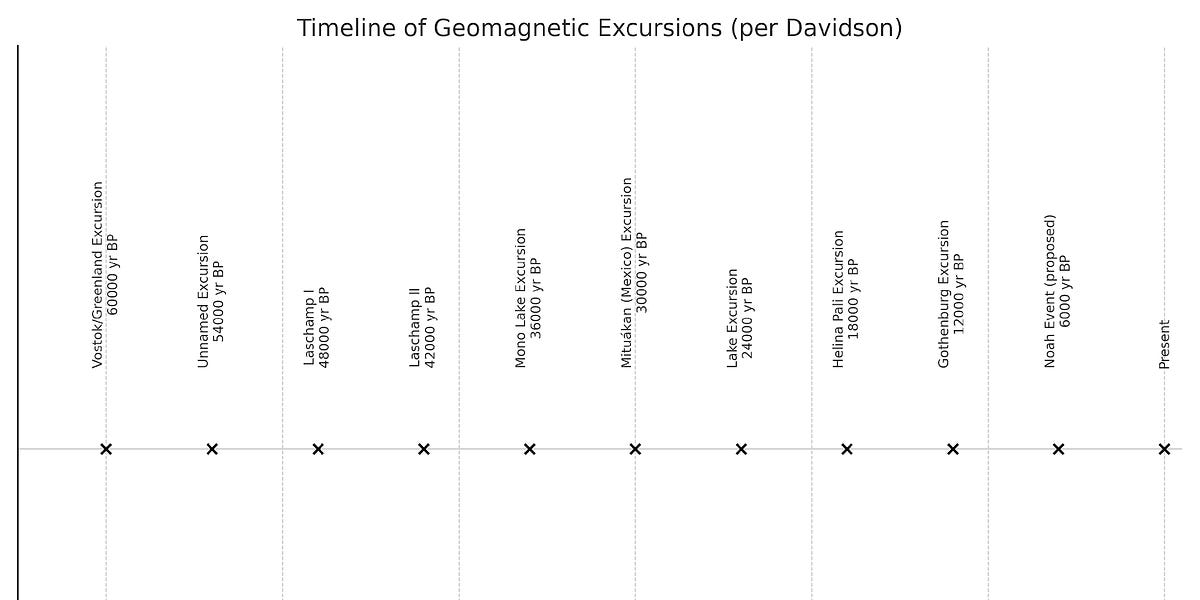
Figure 1. Timeline of past geomagnetic excursions (~60,000 years).
Figure 2. Magnetic pole drift paths, converging near the Bay of Bengal.
Figure 3. Ozone balance disruption: weaker field → ozone loss → more UV.
Figure 4. Carrington-event impact pathway: from solar flare → storm → global disruptions.
 - Wo und wie (No-KYC) #Bitcoin kaufen?
- Wie funktioniert die eigenverantwortliche Selbstverwahrung mit einem HardwareWallet / KeySigner ?
- Wie kannst du Transaktionen selbst-souverän mit eigenem Bitcoin-Node verifizieren?
Bitcoin21Mentor hilft dir. ⚡️
bitcoinmentor.at
- Wo und wie (No-KYC) #Bitcoin kaufen?
- Wie funktioniert die eigenverantwortliche Selbstverwahrung mit einem HardwareWallet / KeySigner ?
- Wie kannst du Transaktionen selbst-souverän mit eigenem Bitcoin-Node verifizieren?
Bitcoin21Mentor hilft dir. ⚡️
bitcoinmentor.at - Wo und wie (No-KYC) #Bitcoin kaufen?
- Wie funktioniert die eigenverantwortliche Selbstverwahrung mit einem HardwareWallet / KeySigner ?
- Wie kannst du Transaktionen selbst-souverän mit eigenem Bitcoin-Node verifizieren?
Bitcoin21Mentor hilft dir. ⚡️
bitcoinmentor.at
- Wo und wie (No-KYC) #Bitcoin kaufen?
- Wie funktioniert die eigenverantwortliche Selbstverwahrung mit einem HardwareWallet / KeySigner ?
- Wie kannst du Transaktionen selbst-souverän mit eigenem Bitcoin-Node verifizieren?
Bitcoin21Mentor hilft dir. ⚡️
bitcoinmentor.at

 I've had this issue previously. What kind of hardware-drive besides SSD 1 or 2 TB would you recommend?
By the way, I have only the basics activated (mempool etc.), no Lightning gadgets or other data-insense apps.
I've had this issue previously. What kind of hardware-drive besides SSD 1 or 2 TB would you recommend?
By the way, I have only the basics activated (mempool etc.), no Lightning gadgets or other data-insense apps.
 $ Trillions from Pension Funds pouring into #Bitcoin soon?
#401k
#RetirementPlan
#PensionFunds
$ Trillions from Pension Funds pouring into #Bitcoin soon?
#401k
#RetirementPlan
#PensionFunds